With today’s advancement in the digital space, companies, institutions, and individuals find online privacy, speed, and security more important than ever.
And one tool that has been used to manage this is the proxy server, but what is a proxy server? We will discuss that in this article.
What Is a Proxy Server?
A proxy server acts as an intermediary between your device and the internet. Instead of connecting directly to a website, your request is routed through the proxy first.
The proxy then communicates with the website on your behalf, retrieves the data, and sends it back to you.
You can think of it as a middleman, as your devices never communicate directly to the internet a proxy system is what they go through.
How Does a Proxy Server work?
A proxy server acts as a middleman between a device and the internet, hiding the real IP address while forwarding requests.
For consumers, they enable privacy, faster browsing via caching, and access to geo-restricted content safely and efficiently.
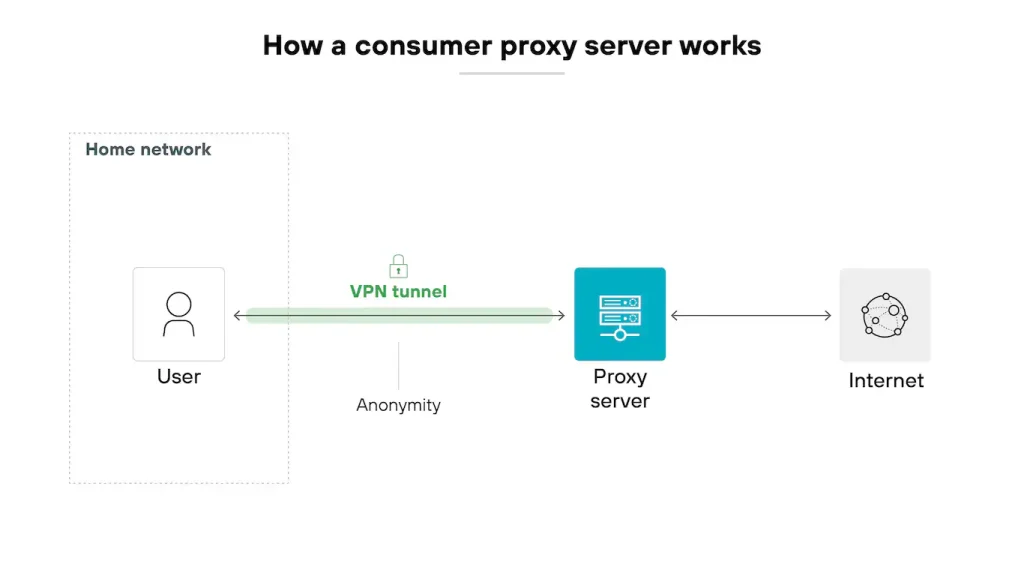
They are slightly different from each other and here are a few points to pick:
- The user sets up a proxy in their operating system or browser.
- The proxy server is used to relay all web requests.
- The proxy sends the request to the destination website after substituting its own IP address for the user’s.
- Depending on user-defined rules, it might filter requests or return cached material.
Also, as we mentioned before consumer proxy server is designed for individuals who want more control, privacy, and flexibility when accessing the internet.
Let’s do a little breakdown of how it works and why people use it.
1. Hides Your Identity
When you connect through a proxy, websites don’t see your actual IP address. Instead, they see the proxy’s IP. This masks your location, offering anonymity and privacy.
2. Bypasses Restrictions
Consumers often use proxies to access geo-blocked content, such as streaming services, websites, or apps restricted in certain regions. Proxies reroute requests through servers in permitted countries.
3. Improves Security
Some proxies filter traffic to block malicious websites, ads, or trackers. This adds a layer of protection between your device and the open internet.
4. Boosts Speed (via Caching)
A proxy can store cached copies of frequently visited websites. When you visit again, it loads faster since it pulls from the proxy rather than the original server.
A business proxy server is tailored for organizational needs, going beyond individual privacy to improve security, control, and efficiency in corporate networks.
Business proxies boost security, manage employee internet usage, and balance server loads for smoother operations. Below are some methods businesses work with proxy servers.
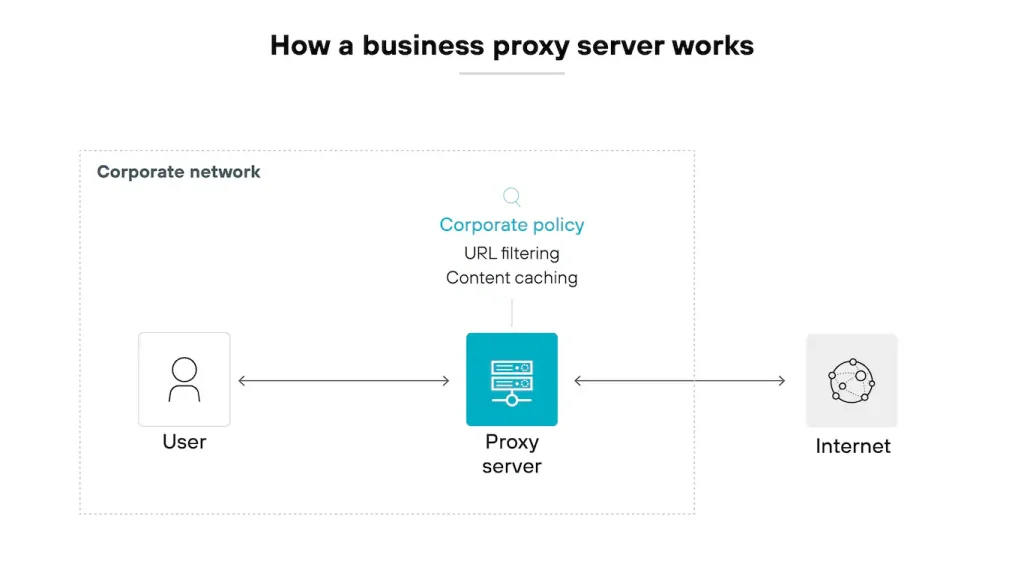
1. Increased Protection
A proxy server hides corporate IP addresses to protect internal systems. Before they reach staff members or servers, it may check traffic for hazards, filter out malicious requests, and block dangerous websites.
2. Control and Management of Networks
Proxy servers are used by businesses to control internet usage. To guarantee productivity and adherence to corporate regulations, they can, for instance, impose data consumption standards, track browser activities, or limit access to websites unrelated to business.
3. Enhancement of Performance
Resources that are regularly visited, such as partner websites or cloud dashboards, can be cached by proxies. This speeds up access and uses less bandwidth, which is important for multinational teams.
4. Utilizing Reverse Proxy and Load Balancing
Incoming traffic can be split equally across several servers by a reverse proxy. This maintains the functionality of apps and webpages.
Types of proxy servers and it uses:
Proxy servers can be grouped according to their function within the network, the types of traffic they handle, or how visible they are to users.
Let’s begin by network role.
Role in network: This refers to whether the proxy acts on behalf of the client or the server:
Reverse Proxy: Sits in front of backend servers and handles incoming requests from external clients. Also for load balancing, TLS termination, and protecting web applications.
Forward Proxy: Sits between internal users and the internet. It forwards client requests, often used for filtering, TLS decryption, and logging. Common in enterprise settings.
Visibility to Users (Transparency): This explains how to classify the way users interact with proxies:
Transparent Proxy: Intercepts traffic without user configuration. It’s “invisible” but still inspects and filters traffic. Ideal for enterprise environments.
Explicit Proxy: Requires manual configuration on the client side. Offers tighter control over traffic but is less seamless for users.
Anonymous Proxy: Masks the user’s IP address to enhance privacy or bypass restrictions. These are more common in consumer use cases and often lack enterprise-grade security.